#LePapierDuMois | august 2024: “Spin current leakage and Onsager reciprocity in interfacial spin-charge interconversion“
By integrating a model that accounts for interface effects, particularly the Rashba-Edelstein effect which converts a charge current into spin density, and bulk effects, such as the spin Hall effect which transforms a charge current into a spin current, Aurélien Manchon, a CNRS research professor at CINaM, and his collaborators from the National University of Singapore offer a new perspective on this phenomenon in their paper published on March 19, 2024.
The conversion between spin currents and charge currents is one of the most widely used mechanisms in spintronics. It enables the manipulation or excitation of the magnetization of a thin magnetic layer with an electric current, or conversely, the use of magnetization dynamics to generate an electric current. This effect offers interesting prospects for applications in spintronics, particularly those envisioned in the PEPR SPIN.
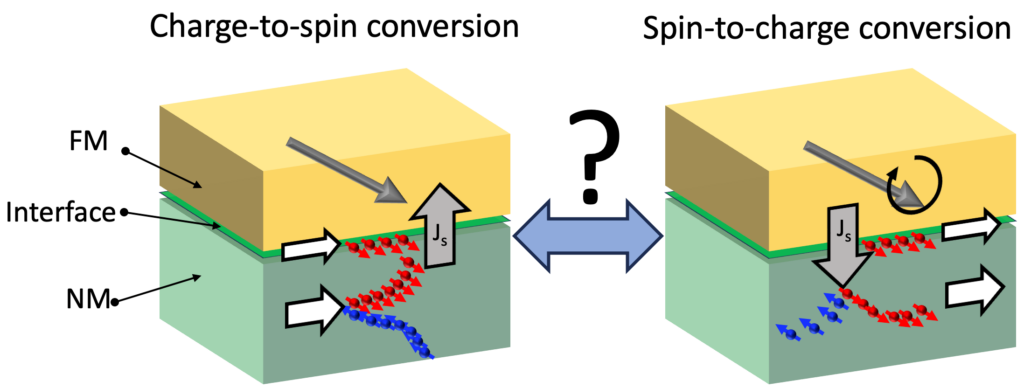
This mechanism has been studied in numerous structures combining heavy metals or topological materials. However, experimental results show significant disparity, and in systems involving topological insulators, the spin-charge and charge-spin conversions do not appear equivalent, which seems contradictory to Onsager’s reciprocity principle. This principle states that in a linear regime, the coefficients describing two reciprocal physical effects must be equal.
Relying on a model that accounts for interface effects (the Rashba-Edelstein effect, which converts a charge current into spin density) and bulk effects (the spin Hall effect, which converts a charge current into a spin current), Aurélien Manchon and collaborators from the National University of Singapore shed new light on this central phenomenon in spintronics. They demonstrated that the leakage of spin current in the non-magnetic metal leads to asymmetric spin-charge interconversion processes. In particular, spin-charge conversion is much less sensitive to the absorption of spin current in the non-magnetic metal than charge-spin conversion. This observation suggests that spin pumping is a more reliable technique for extracting the interfacial Rashba parameter than the spin-orbit torque technique.
This paper was published in Physical Review B and selected for the Editor’s Suggestion.
Co-auteurs : Shuyuan Shi, and Hyunsoo Yang


